Creating a Board Skills Matrix
An essential question asked by board members is how can we improve our performance? While there are many possible answers to solve this riddle, making sure your board composition is set-up as intended is key. An increasingly prevalent tool used by boards in evaluating their board’s composition is the Board Skills Matrix. According to a 2017 study by Equilar, 307 U.S. and Canadian public companies disclosed the use of a Skills Matrix within their proxy statement. A Board Skills Matrix strengthens an organization’s overall governance practices by identifying the current skills, knowledge, experience and capabilities of current board members. The matrix is a relatively simple table that lists all board members along the top with a board’s view of the essential skills and experience required by the board to be most effective.
Once the essential skills are determined, the board can then evaluate whether each board member possesses that skill or not with a simple check mark (see example below). This evaluation can be done, by the Board or Nominating Committee Chair, by conducting their own assessment of each board member or by asking each board member to self-assess against the identified skills and experiences through use of a questionnaire. At GGA, we have developed a digital boardroom platform, the emPower platform, which can be used by boards to identify the skills and experiences they require. Then each board member can fill out an online self-assessment questionnaire on how they stack up against the identified skills and experiences. These individual questionnaire results can be consolidated and instantly accessed by the Board or Nominating Committee Chair to identify any gaps amongst the current board.
Illustrative Example: Board Skills Matrix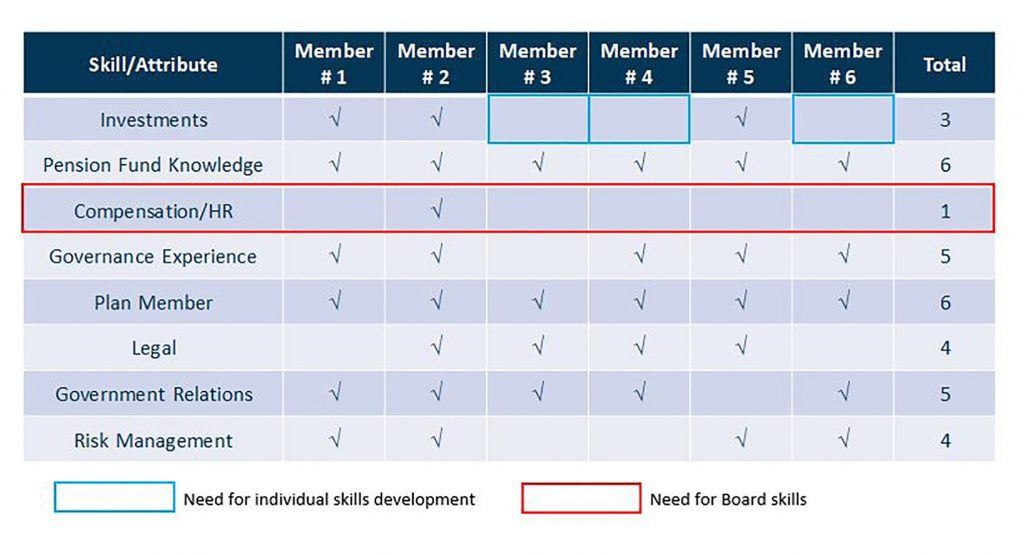
A completed skills matrix, as demonstrated above, helps the board in two ways:
- Board Member Development – the matrix identifies areas for individual skills development, that can be strengthened through additional education and training opportunities. This allows for an individual development plan to be created to improve the board member’s overall skill level.
- Board Skills Development – the matrix can identify areas for overall board improvement through education or through the recruitment of a new board member that possesses a specific skill set to improve the board’s composition.
In the example above, Board Members # 3, 4 and 6 could use individual skills development in the area of Investments. Increased skill/experience in Compensation and Human Resource matters is required for the board, as many board members do not have experience in that area.
At a bare minimum, the results of the Board Skills Matrix assessment should be shared internally so that the board can identify any areas for future improvement. However, many public companies are taking a pro-active approach and disclosing the results of the assessment directly in their proxy statements on an annual basis (as evidenced by Equilar’s research above). For mid and large cap companies, shareholders are expecting more transparency from companies which require companies to be honest about the skills and experience the board truly values and how each board member stacks up. They can also use this opportunity to detail to shareholders how the board plans on filling any identified gaps in skills.
How does a board determine which skills and experiences to include within its skills matrix? It starts by asking where the organization is today and where it wants to be in the future? Are the skills required to sit on the board today going to be the skills required 5 years from now? This allows the board to determine the skills required to sit on the board and add value, both now and in the future. There are certain skills that are commonly required for a board such as Financial Literacy, Human Resources and Legal experience, but boards should also ask what industry-specific skills and experience are required in addition to functional experience. Are there diversity aspects that need to be considered by the board in addition to specific skill sets? These questions should all be answered when developing a skills matrix.
Required Board Skills
What skills should you be looking for? Recent research by Korn Ferry indicates that the Top 5 skills required by boards as part of their Board Skills Matrix are as follows:
- Finance/Accounting (97% prevalence)
- Industry Knowledge (95% prevalence)
- Compensation/HR (86% prevalence)
- Board/Governance Experience (81% prevalence)
- Legal/Regulatory/Compliance/Government/Public Policy (80% prevalence)
Other skills/experience included by companies are:
- M&A/Corporate Finance/Investment Banking/Capital Markets (74% prevalence)
- Risk Management (64% prevalence)
- Executive Leadership (63% prevalence)
- Strategic Planning (48% prevalence)
- International Experience (45% prevalence)
While not identified above, a growing number of companies are also including Cyber-Security and Information Technology experience on their boards to deal with the increasingly concerning issue of cyber-hacking.
Diversity & Matrix Development
Historically, companies produce a long “laundry list” of skills and experiences as part of their Board Skills Matrix. However, institutional investors are starting to advocate for a more nuanced approach to developing a skills matrix. Instead of including 10-15 different skills and/or experience, they prefer to see companies disclose the 3-5 most important skills required on the board with an evaluation of how each board member compares against these skills. This makes it more clear which skills and experiences the board feels add the most value and how the current set of board members adequately cover each of those skills/experiences.
In addition to skills and experiences, companies are also looking at ways to increase the diversity on their board and will sometimes include this as one of the board considerations when evaluating board composition. While quota-based systems have been implemented in many European countries, they have historically not made their way across the Atlantic to North America. However, recent trends indicate a growing focus on gender diversity in North America, with California recently approving a quota-based system for public companies incorporated or headquartered in the state. In Canada, the Toronto Stock Exchange (“TSX”) has implemented a comply or explain regime that requires companies to disclose the existence of a gender diversity policy for executives and board members or explain why a policy has not been put in place. ISS and Glass Lewis have also put in place specific voting recommendation guidelines that will recommend “Against” votes for Nominating Committee Chairs in situations where there is no written diversity policy and no female board members. These new laws and policies should cause boards to consider diversity within their matrix in order to stay in line with this evolving trend. Diversity should also go beyond just gender to include age, race, religion and ethnicity as well.
Closing Thoughts
Getting the composition of your board right is a tough job, especially with the evolving nature of the world as we transition to a more digital world and deal with emerging issues such as climate change, cyber-security and sustainability. It is important for boards to put in the proper processes in place to ensure they are operating efficiently and effectively. One of the essential tools in doing this is the development of a well thought out Board Skills Matrix to identify the skills and experiences required and evaluating your board members against this criteria. By using this tool, boards can prepare themselves to deal with a company’s major issues, both today and into the future, thereby acting in the best interests of stakeholders.
Like what you read? Feel free to browse through the rest of our blog content (how about checking out The Power of Board Assessments) for more.
