GGA’s Annual CEO Pay for Performance Survey with the Globe and Mail
GGA and the Globe and Mail partnered once again to present our annual ranking of CEO compensation for the 100 largest public companies in Canada’s S&P/TSX composite Index.
Full results here.
Key Findings
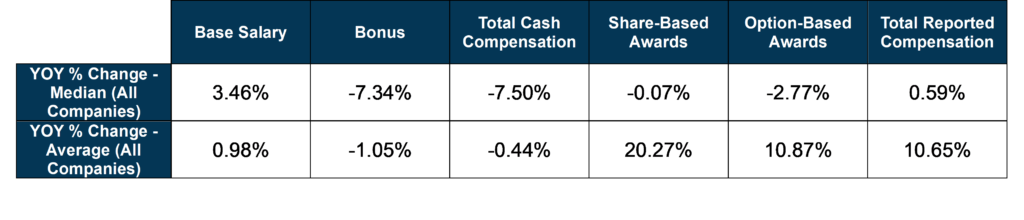
- Average total reported compensation increased by ~10% while the median total reported compensation remained flat
- The majority of the total compensation increase was tied to an average 20% and 11% increase in share- and option-based awards respectively, further increasing the weighting of CEO compensation on long-term, at-risk compensation
- The highest paid CEO, in this year’s study, was Patrick Dovigi of GFL Environmental Inc ($68.46 Million).
- The second and third highest paid CEO’s were granted about half the value of the highest paid CEO at $37.7M and $36.8M.
- Performance vesting share-based awards (“PSUs”) were the most prevalent form of long-term incentive-based compensation (“LTIP”), granted at 79% of companies.
- Among the 85 companies that awarded a cash bonus to the CEO, 67% (N=57) paid above the target level, indicating generally strong operating performance in 2023 at these companies.
- Female CEOs were still underrepresented, accounting for 4% of all CEOs (down from 5% in 2022) in this year’s study.
- Average annual total shareholder return was 15% (up from 4% in 2022).
There is an increased weighting on share-based awards over option-based awards. This continues a trend observed by GGA in recent years amongst the largest companies in Canada.
Our analysis shows that share-based compensation is the major reason why CEO pay is climbing in Canada. Of the 100 companies included in the ranking, 77 granted multiple forms of LTIP in 2023, compared to 73 in 2022. The LTIP, which refers to the long-term incentive component of the CEO’s compensation package, includes options and share-based awards such as PSUs and Restricted Share Units (“RSUs”) which vest solely over time with no additional performance conditions. In recent years, we have been observing an increasing prevalence of PSUs, a form of equity compensation that vests only if certain performance criteria are met which is designed to better align CEO pay to shareholder value generation over time.
With growing emphasis on share-based compensation, we have seen a shift away from options. GGA’s Peter Landers discussed this trend in an interview with the Globe and Mail, stating, “There definitely is a movement away from options, just because the nature of the scrutiny they’re under by institutional shareholders, tax implications and the lack of ability to really grow and make those stock options worthwhile to the individuals.” When looking at our data, we see that 43 companies in the top 100 did not grant any options in 2023. In cases where companies award options, they generally only tend to account for 25% of the LTIP grant, with the remaining 75% being allocated to PSUs and/or RSUs. This trend is expected to continue as Canada’s increased capital-gains tax inclusion rate takes into effect, making stock options even less attractive in the future.
Full story here.
Reach out to us at Global Governance Advisors to learn how our board services can help you address regulatory and shareholder challenges related to executive compensation.
